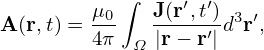
Given a current source J(r,t), the vector potential can be calculated using
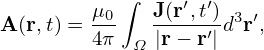 | (634) |
where
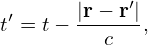 | (635) |
is called the retarded time. For a steady-state source, J(r′,t′) = J(r). Then Eq. (634) is simplified as
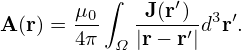 | (636) |
For a current flowing in a thin wire, the above equation is written as
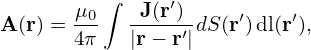 | (637) |
where dS is a surface element perpendicular to the wire and dl is a line element along the wire. Using J(r′)dS(r′) = I(r′), the above eqaution is written as
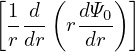
 | (639) |
(Aϕ is needed in several applications. In solving the free-boundy equilibrium problem, we need to calculate Aϕ generated by the PF coils. In studying the effects of RMP on particles, we need to calculate Pϕ, the canonical toroidal angular momentum, whose defintion involves Aϕ. Then we need to calculate Aϕ generated by the RMP coils.)
A PF coil at (R′,Z′)with current I (a filamentary current loop) contributes to Aϕ at ϕ = 0 via
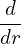 | (640) |
Sine Aϕ is axsymmetric, the above formula applies to all values of ϕ. Set I = 1, we get Green’s function: