Next: Surface operator acting on Up: Flux coordinate system Previous: Surface differential operators
A perturbation
![]() must be a periodic function of the
poloidal angle
must be a periodic function of the
poloidal angle ![]() and toroidal angle
and toroidal angle ![]() , and thus can be expanded
as the following two-dimensional Fourier series,
, and thus can be expanded
as the following two-dimensional Fourier series,
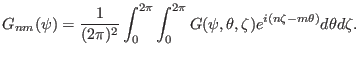 |
(171) |