Next: Expression of normal curvature Up: Numerical results for EAST Previous: Numerical results of global
In this section, we derive formulas for calculating the geodesic curvature and
normal curvature in magnetic surface coordinate system
![]() .
The derivation looks tedious but the final results are compact (especially for
the geodesic curvature
.
The derivation looks tedious but the final results are compact (especially for
the geodesic curvature ![]() ). The magnetic curvature is defined by
). The magnetic curvature is defined by
![]() , which can be further
written as
, which can be further
written as
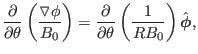 |
(264) |
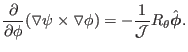 |
(265) |
![$\displaystyle \frac{\Psi'^2}{B_0} \mathcal{J}^{- 1} \left\{ \left[
\frac{\parti...
...rac{\mathcal{J}^{-
1}}{B_0} Z_{\theta \theta} \right] \hat{\mathbf{Z}} \right\}$](img746.png) |
|||
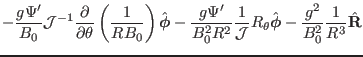 |