Next: Safety factor Up: Axisymmetric magnetic field Previous: Closed magnetic surfaces in
This section introduces parameters that characteristic the shape of the
projection of a magnetic surface on the poloidal plane. The ``midplane'' is
defined as the plane that passes through the magnetic axis and is
perpendicular to the symmetric axis (![]() axis). For a up-down symmetric (about
the midplane) magnetic surface, its shape can be roughly characterized by four
parameters, namely, the
axis). For a up-down symmetric (about
the midplane) magnetic surface, its shape can be roughly characterized by four
parameters, namely, the ![]() coordinate of the innermost and outermost points
on the midplane,
coordinate of the innermost and outermost points
on the midplane,
![]() and
and
![]() ; the
; the ![]() coordinators of the highest point of the magnetic surface,
coordinators of the highest point of the magnetic surface,
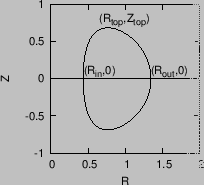
![]() . These four parameters are indicated in Fig. 4.
. These four parameters are indicated in Fig. 4.
 |
In terms of these four parameters, we can define the major radius of a magnetic surface
The four shape parameters for the typical Last-Closed-Flux-Surface (LCFS) of
EAST tokamak are: major radius
![]() (can reach
(can reach ![]() ), minor
radius
), minor
radius
![]() , ellipticity
, ellipticity
![]() (can be in the range from 1.7
to 1.9), triangularity
(can be in the range from 1.7
to 1.9), triangularity
![]() (can be in the range from 0.5 to 0.7).
Note that the major radius
(can be in the range from 0.5 to 0.7).
Note that the major radius ![]() of the LCFS is usually different from
of the LCFS is usually different from
![]() (the
(the ![]() coordinate of the magnetic axis). Usually we have
coordinate of the magnetic axis). Usually we have
![]() due to the Shafranov shift.
due to the Shafranov shift.
yj 2018-03-09