Next: Linearized ideal MHD equation Up: MHD equations Previous: Eliminating mass density from
For the convenience of reference, the MHD equations discussed above are
summarized here. The time evolution of the four quantities, namely
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , are governed respectively by the
following four equations:
, are governed respectively by the
following four equations:
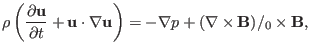 |
(20) |
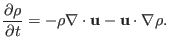 |
(22) |