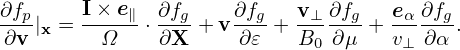
Expand the distribution function fg as
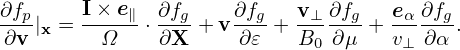 | (47) |
where Fg is assumed to be an equilibrium distribution function, i.e.,
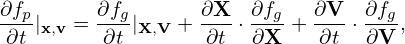 | (48) |
Using Eqs. (47) and (48) in Eq. (42), we obtain an equation for δFg:
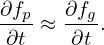 | (49) |