Next: Jacobian for straight-field-line poloidal Up: Calculating coordinate Previous: Jacobian for equal-arc-length poloidal
The volume element in
![]() coordinates is given by
coordinates is given by
![]() . If we choose a Jacobian that is
independent of
. If we choose a Jacobian that is
independent of ![]() , then uniform
, then uniform ![]() grids will correspond to grids
with uniform volume interval. In this case,
grids will correspond to grids
with uniform volume interval. In this case,
![]() is written as
is written as
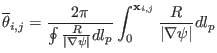 |
(198) |
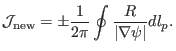 |
(199) |
yj 2018-03-09