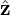
To calculate the divergence of a vector, it is desired that the vector should be in the contravariant form because we can make use of the fact:
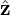 | (107) |
for any scalar quantities α and β. Therefore we write vector A as
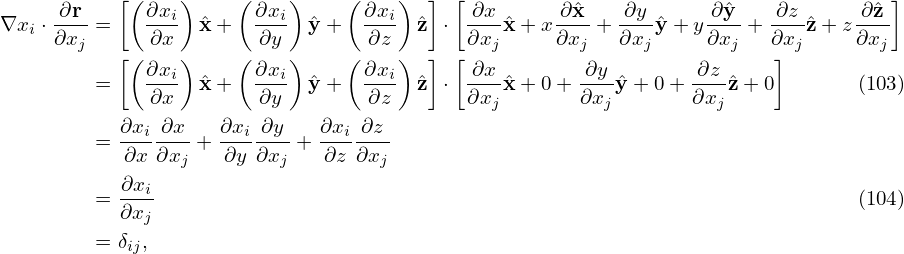 | (108) |
where A(ψ) = A ⋅∇ψ, A(𝜃) = A ⋅∇𝜃, A(ζ) = A ⋅∇ζ. Then the divergence of A is readily calculated as
where the second equality is obtained by using Eqs. (103), (104), and (105).