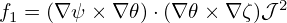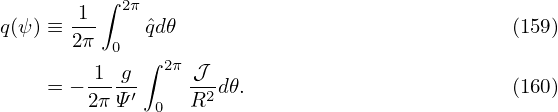
The global safety factor defined in Eq. (37) is actually the poloidal average of the local safety factor, i.e.,
Note that q and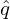 defined this way can be negative, which depends on the choice of the positive
direction of ϕ and 𝜃 coordinates (note that the safety factor given in G-eqdsk file is always positive, i.e.
it is the absolute value of the safety factor defined here).
defined this way can be negative, which depends on the choice of the positive
direction of ϕ and 𝜃 coordinates (note that the safety factor given in G-eqdsk file is always positive, i.e.
it is the absolute value of the safety factor defined here).
Next, let us transform the 𝜃 integration in expression (160) to a curve integral in the poloidal plane. Using the relation dℓp and d𝜃 [Eq. (168)], expression (160) is further written
Expression (161) is used in the GTAW code to numerically calculate the value of q on magnetic surfaces (as a benchmarking of the q profile specified in the G-eqdsk file). Expression (161) can also be considered as a relation between q and g. In the equilibrium problem where q is given (fixed-q equilibrium), we can use expression (161) to obtain the corresponding g (which explicitly appears in the GS equation):
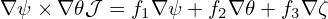 | (162) |
We note that expression (162) involves magnetic surface averaging, which is unknown before we know Ψ. Therefore iteration is usually needed in solving the fixed-q equilibrium (i.e., we guess the unknown Ψ, so that the magnetic surface averaging in expression (162) can be performed, yielding the values of g.)
Using Bp = |∇Ψ|∕R and Bϕ = g∕R, the absolute value of q in expression (161) is written